Aerosol administration during noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a common clinical drug administration method, but the drug administration efficiency of different drug delivery devices is different.
In a study, subjects were asked to inhale 2.5 mg of salbutamol labeled with 99mTc-DTPA (25 mCi/3 mL), 0.25 mg of ipratropium bromide, and 0.9% saline using a mesh nebulizer and a jet nebulizer, respectively. The pulmonary aerosol deposition was evaluated using planar scintigraphy from the start of the nebulization timer for 1 minute or until no visible aerosol (whichever occurred first).
The results showed that compared with the jet nebulizer, the nebulization drug administration effect of the mesh nebulizer during NIV was significantly better, and the image contrast was obvious.
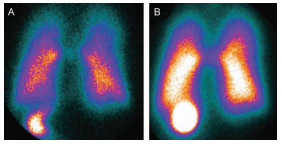
A. Jet nebulizer; B. Mesh nebulizer
Reference: Galindo-Filho VC, Ramos ME, Rattes CSF, et al. Radioaerosol pulmonary deposition using mesh and jet nebulizers during noninvasive ventilation in healthy subjects. Respir Care. 2015;60(9):1238-1246