
Budesonide is a medication used to manage and treat inflammatory diseases, mainly affecting the airways and gastrointestinal tract. It is in the corticosteroid class of medications. Clinicians are accustomed to adding budesonide suspension for inhalation to normal saline for nebulization. It is worth studying whether the particle size and zeta potential of the diluted budesonide suspension will affect the physical properties of the drug solution and whether it will affect the clinical efficacy.
A study analyzes the in vitro characteristics of inhaled budesonide suspension with different concentration gradient particle size and zeta potential, and compares the clinical efficacy, for providing the rational use of inhaled suspension in clinics with evidence-based medical evidence.
METHODS
According to the dilution times of budesonide suspension in clinical practice, the undiluted group, 1-fold dilution group, 2-fold dilution group, and 4-fold dilution group of budesonide suspension were set( n = 20). The changes of suspension particle size, zeta potential, and clinical efficacy of the four groups were compared.
RESULTS
The particle size of budesonide suspension with different concentration gradients changed significantly. There was a significant difference( P<0.000 1) between the undiluted group ( 4 075±60) nm and the 1-fold dilution group ( 1 557±132) nm, and there was a significant difference ( P<0.01) between the double dilution group ( 1 557±132) nm and the 2-fold dilution group ( 1 067±233) nm. At the same time, there was no significant difference between the 2-fold dilution group and the 4-fold dilution group. With the increase in dilution ratio, the zeta potential of budesonide suspension became extremely unstable, and the clinical efficacy gradually decreased.
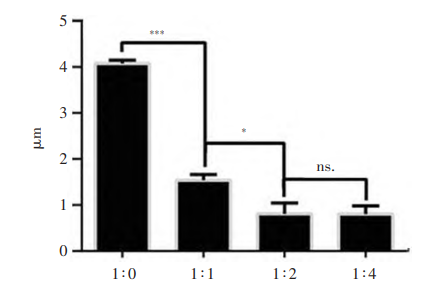
Changes in particle size of budesonide suspensions at different concentration gradients
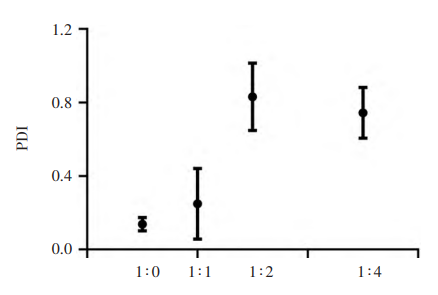
Changes in the Potential of Budesonide Suspensions at Different Concentration Gradients
CONCLUSION
The difference in concentration gradient can significantly affect the particle size and zeta potential of budesonide suspension, which may cause the decrease in titer.In order to ensure clinical efficacy, the diluted solvent of budesonide suspension for inhalation should not exceed 1 time of the original solution.
Reference
[1] Feng Q,Xiao H,Zheng C,et al.Immunosuppressive triangle depletion through the combination punches strategy for enhanced immunotherapy.Applied Materials Today,2022,26: 1013-1015.
[2] Chen C M,Chang C H,Chao C H,et al.Biophysical and chemical stability of surfactant /budesonide and the pulmonary distribution following intra-tracheal administration[J].Drug Delivery,2019,26( 1) :604-611.
[3]Wang H M.Analysis of ultrasonic atomized inhalation of antibiotics in infant pneumonia treatment.[J].Pak J Pharm Sci,2018,31:1653-1657.